Voltage testing
What it is used for:
The voltage test allows you to determine what condition the battery and voltage regulator are in.
The test allows you to read the voltages on the battery in the various operating modes of the car:
- the voltage of the battery at a standstill
- voltage drop when starting a car
- the state of charge during slow-motion operatio
- charging status during operation under load
The test procedure consists of:
- Performing a calibration, reading the battery voltage at rest using an electronic multimeter. This procedure allows you to calibrate your interface so that the voltage values it reads are as close as possible to the actual values.
- Perform a given test to determine the efficiency of the battery in a particular operating mode.
- Interpret the result to determine whether action is required to recharge or replace the battery.
What steps should be taken in the event of a negative test result?
- Perform the test again
- Recalibrate the interface
- Assess whether your interface is of the right quality
- Recharge the battery
- Consider battery replacement
Diagnostic monitors
Diagnostic monitors are a superior diagnostic option. It provides quick, simple and very valuable information on the condition of the vehicle.
With its help, we can find out whether a fault is present and whether it has been correctly rectified.
We can also find out whether the fault codes have been cleared in order to hide the damage to the vehicle.
In addition, it will warn us of serious faults that occur sporadically.
What does the colour of the car icon mean?
- Green – no fault codes and all available monitors completed.
- Yellow – no fault codes and there are uncompleted monitors.
- Red – error codes are present and there are unfinished monitors.
What if a monitor is uncompleted?
This means that a particular diagnostic procedure has not been completed.
Continuous monitors are monitored all the time and are faulted and tested relatively quickly, e.g. loss on ignition. When it comes to discontinuous monitors, the time is longer as a number of conditions must be met for the diagnostic system to carry out the full procedure, e.g. catalytic converter fault.
In the case of an uncompleted monitor, special care must be taken, as we do not know whether its test will result in a recurrence of the fault or whether the system still needs time for additional tests.
G-Sensor
A function that allows the user to check gravitational force in the car based on a clock. The function is intended to enable the user to read the current g-force while driving. The function shows the current and maximum value.
Did you know…?
When driving an F1 car, the driver is subjected to various levels of g-force. During acceleration it is usually 2g, during braking around 5g and in corners between 4 and 6g.
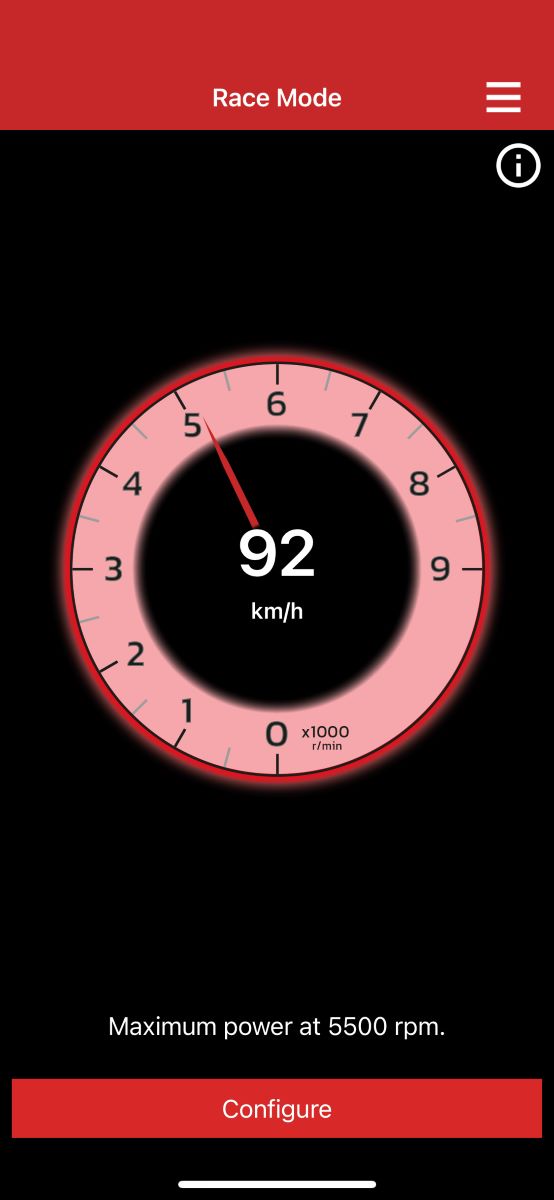
Race mode
Race mode is a configurable function that allows visual and audible signals to be assigned to a user-defined engine speed value. It is possible to set the function so that gear changes take place at the best moment in terms of acceleration. Information on what RPM the engine reaches its maximum power should be sought from publicly available sources, such as internet forums or newspaper articles.
What does Race mode offer?
Race mode allows optimal gear changes for the most efficient acceleration of the vehicle.
Configuration:
To configure Race mode correctly, you need to enter the rpm at which the car reaches its maximum power
Mode of operation:
- A single beep and the blinking of the clock informs you to prepare to shift into a higher gear
- A double beep and a steady red illumination of the clock indicate the need to shift up a gear immediately.